Imixs-Workflow Adapter API
The Imixs-Workflow Adapter API is part of the microkernel architecture pattern providing an extension mechanism to adapt the processing life cycle of a BPMN Event. An Adapter class can execute business logic and adapt the data of a process instance. For example, an adapter can call an external Microservice to send or receive data.
Adapters can be implemented either as a SignalAdapter or GenericAdapter class. Depending on its type, the Adapter class is executed before or after the plug-in processing life-cycle, controlled by the WorkflowKernel:
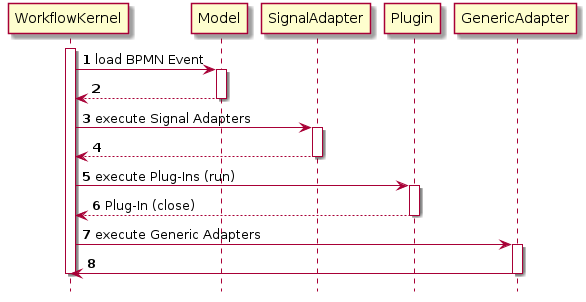
SignalAdapter
The SignalAdapter is defined by the Interface:
org.imixs.workflow.SignalAdapter
In different to the Plugin API the SignalAdapter is bound to a single Event within a BPMN 2.0 model. This allows a fine grained configuration.
The BPMN signal definition contains the adapter class name:
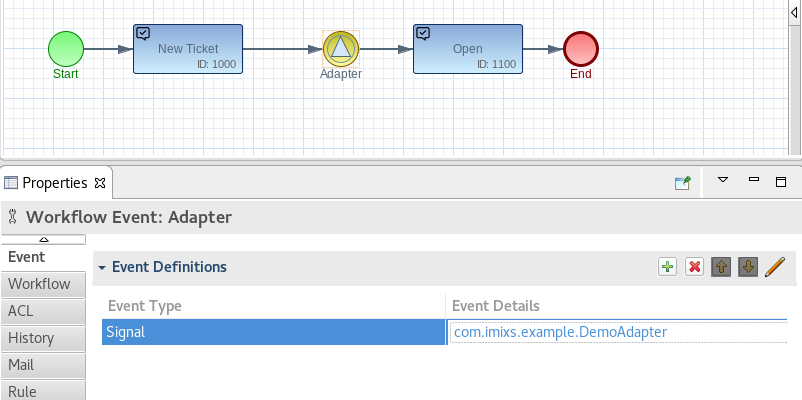
Note: The SignalAdapter is executed before the Plug-In processing life-cycle.
GenericAdapter
The GenericAdapter is defined by the Interface:
org.imixs.workflow.GenericAdapter
This Adapter can be used to execute general business logic independent from the BPMN model. A GenericAdapter should not be associated with a BPMN Signal Event.
The GenericAdapter is executed after the Plug-In processing life-cycle.
How to Implement an Adapter
The Imixs Adapter-API defines the call-back method ‘execute’. This method is called by the WorkflowKernel:
public ItemCollection execute(ItemCollection document,ItemCollection event) throws AdapterException;
CDI Support
The Imixs-Workflow Adapter API also supports CDI. In this way an EJB or Resource can be injected into an adapter class by the corresponding CDI annotation. See the following example:
public class DemoAdapter implements SignalAdapter {
// inject services...
@Inject
ModelService modelService;
...
@Override
public ItemCollection execute(ItemCollection document, ItemCollection event) throws AdapterException {
List<String> versions = modelService.getVersions();
....
}
}
In this example the adapter injects the Imixs ModelService to ask for available model versions.
Exception Handling
An adapter can also extend the processing phase by throwing an AdapterException. For example in case of a communication error an Adapter could send and error code back to the processing life cycle.
See the following example handling a jax-rs client communication:
public ItemCollection execute(ItemCollection workitem, ItemCollection event) throws AdapterException {
...
// call external Rest API....
try {
Response response = client.target(uri).request(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
.post(Entity.entity(data, MediaType.APPLICATION_XML));
} catch (ResponseProcessingException e) {
throw new AdapterException(
MyAdapter.class.getSimpleName(),ERROR_API_COMMUNICATION,"Failed to call rest api!");
}
.....
}
In this example an Adapter throws an AdapterException when the Rest API call failed. The Exception contains the Adapter name, an Error Code, and a Error Message. The processing life-cycle will not be interrupted by an AdapterException. But the Exception information will be added into the current process instance in the following items:
- adapter.error_code - the exception code
- adapter.error_message - the exception message
- adapter.error_cause - the exception cause
- adapter.error_params - optional exception params provided by the AdapterException
These data can be used to control the processing flow. For example a conditional event can evaluate the adapter.error_code to control the outcome of the event.
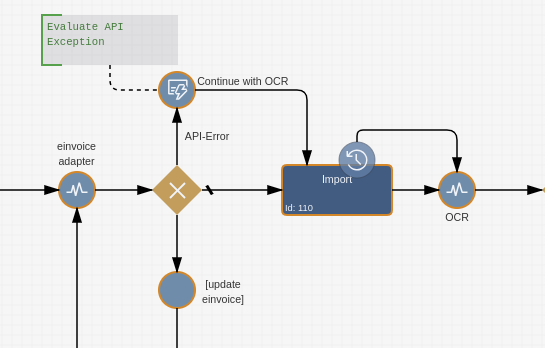
Just add an conditional sequence flow to query your exception
"" != workitem.getItemValueString("adapter.error_code");
Of course, a Plugin can investigate the Adapter Exception data and interrupt the processing life-cycle by throwing a PluginException. In this case a running transaction will be automatically rolled back.
public ItemCollection run(ItemCollection documentContext, ItemCollection adocumentActivity)
throws PluginException {
....
if (documentContext.hasItem("adapter.error_code") {
throw new PluginException(documentContext.getItemValueString("adapter.error_context"),
documentContext.getItemValueString("adapter.error_code"),
documentContext.getItemValueString("adapter.error_message")
);
}
}
If you want to interrupt the processing immediately, your Adapter Implementation can throw either a PluginException or a ProcessingErrorException
A PluginException is handled the same way as defined in the Plugin API and can be handled by the workflow application. An ProcessingErrorException interrupts the processing life cycle immediately.
public ItemCollection execute(ItemCollection workitem, ItemCollection event) throws AdapterException {
...
// call external Rest API....
try {
Response response = client.target(uri).request(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
.post(Entity.entity(data, MediaType.APPLICATION_XML));
if (response==null)
// interrupt the processing life cycle
throw new PluginException(
MyAdapter.class.getSimpleName(),ERROR_API_COMMUNICATION,"An error occurred...");
} catch (ResponseProcessingException e) {
// interrupt current transaction
throw new ProcessingErrorException(
MyAdapter.class.getSimpleName(),ERROR_API_COMMUNICATION,"Failed to call rest api!");
}
.....
}
In both cases the running transaction will be automatically rolled back.
